How to choose an industrial LCD screen with appropriate brightness?
Date:2025-09-28
Choosing a suitable brightness LCD screen for industrial equipment is a crucial and must be tailored to local conditions. Improper brightness selection can directly result in the device being unusable in the target environment.
The core of choosing the brightness of industrial LCD screens is to ensure that the displayed content can be read clearly, comfortably, and accurately in any usage environment.
1. Core principle: Determine based on the lighting conditions of the usage environment
The selection of brightness (in nits or cd/m ²) directly corresponds to the lighting environment in which your device will operate. You can quickly locate the brightness range you need based on the following flowchart:
The above scope is a common standard in the industry, which you can use as the cornerstone of your selection.
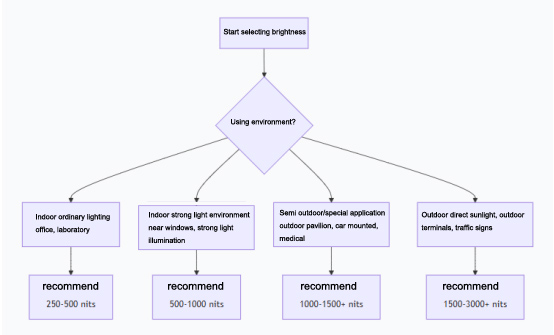
The above scope is a common standard in the industry, which you can use as the cornerstone of your selection.
2. In depth analysis: brightness selection in different environments
In order to give you a deeper understanding of why you chose this, the following are detailed explanations for different scenarios:
Usage environment | Recommended brightness | Explanation and Typical Scenarios |
Indoor ordinary environment | 250 - 500 nits | Explanation: This is the standard brightness for most indoor environments, providing a comfortable viewing experience. Typical scenarios: factory control room, office computer, laboratory equipment, indoor bank ATM, indoor self-service inquiry machine. |
Indoor strong light environment | 500 - 1000 nits | Explanation: The ambient light is strong and requires higher brightness to counteract reflections and ensure clear content. Typical scenarios: Automated ticket vending machines near windows, production line workstations with strong lighting, indoor retail POS machines, medical monitors (clearly visible in bright wards). |
Semi Outdoor&Special Applications | 1000 - 1500+ nits | Explanation: Being under an outdoor sunshade or inside a car can be affected by a large amount of ambient light. Typical scenarios: Outdoor information kiosks (with roofs), charging stations, onboard central control/dashboard, maritime equipment. High brightness ensures readability during most of the daytime. |
Outdoor direct sunlight | 1500 - 3000+ nits | Explanation: This is the highest requirement, and a high brightness screen must be used to counteract strong direct sunlight, otherwise the screen content will completely 'disappear'. Typical scenarios: outdoor industrial control terminals, traffic signs, outdoor advertising machines, construction site equipment. |
3. Beyond brightness: a key factor closely related to brightness
When selecting brightness, one must not only look at the nitt value, but also consider the following points simultaneously:
Anti glare and full lamination technology:
Anti glare (AG) surface treatment: roughening the glass surface through chemical or physical means, converting specular reflection into diffuse reflection, thereby weakening the interference image caused by ambient light. For applications with medium to high brightness (above 500 nits), it is strongly recommended to choose AG processing.
Optical full bonding: Fully bond the LCD glass to the surface cover (touch screen) with optical adhesive. This can significantly reduce the reflection and refraction inside the screen, improve contrast and visibility, especially in strong light. The actual visual effect of the screen after lamination is much better than that of the screen without lamination at the same brightness.
Readability and Contrast:
Core principle: Screen readability=brightness+contrast.
A screen with low contrast in a dark room, even with high brightness, will appear grayish under strong light. Therefore, while focusing on brightness, it is also important to pay attention to the contrast parameters of the screen (such as 1000:1), and choose a screen with wide viewing angle (IPS/FFS) technology to ensure that color and contrast do not significantly decrease when viewed from different angles.
Power consumption and thermal management:
Brightness is the main source of power consumption for LCD screens. The higher the brightness, the greater the power consumption, and the more heat is generated.
For portable devices, high brightness will quickly consume battery power.
In industrial environments, high temperatures may affect screen lifespan and stability. Therefore, it is necessary to strike a balance between readability and power consumption/heat dissipation, avoiding the meaningless pursuit of excessively high brightness.
Cost considerations:
The cost of increasing brightness by one level almost increases exponentially. A 2000 nits screen may cost several times more than a 500 nits screen. Be sure to choose according to actual needs to avoid cost waste.
4. Common selection misconceptions
Misconception 1: The higher the brightness, the better.
Correction: In dark or ordinary indoor environments, excessive brightness (such as 1000 nits) can cause visual fatigue, eye pain, and reduce readability. It will also bring unnecessary power consumption and costs.
Misconception 2: Only look at the peak brightness on the specification sheet.
Correction: Some manufacturers may label "peak brightness", which may be a value achieved in a short period of time under specific conditions. Be sure to confirm that it is labeled with standard brightness or sustainable working brightness.
Misconception 3: Ignoring reflection processing.
Correction: In strong light environments, "anti reflection" is more important than "high brightness". A 500 nits screen with good AG processing and full lamination technology may have better actual visual effects than a 1000 nits screen without any processing and with severe reflection.
Summary and Decision Checklist
Steps for selecting brightness:
Define the environment: Clearly define the primary lighting conditions for the use of the equipment.
Determine the reference brightness: Refer to the table above to find the corresponding brightness range.
Assessment auxiliary technology: If the ambient light is complex, it is necessary to select "anti glare (AG) treatment" and "optical full lamination" for the screen.
Trade offs: Consider power consumption, heat dissipation, and cost, and choose the most economical solution while ensuring basic readability.
Request for sample testing: Before making a final decision, it is essential to request screen samples from the supplier and conduct testing in real or simulated usage environments. This is the most reliable method.
I hope this detailed guide can help you make wise decisions. If you can share the specific usage scenarios of the device (such as "outdoor gas station touch screen" or "control panel on the side of the machine tool"), I can provide you with more specific brightness suggestions.
industrial LCD screen:https://www.auo-lcd.com/




