Why can't the working temperature of the LCD screen reach 90 ℃?
Date:2025-12-18
Why can't the working temperature of the LCD screen reach 90 ℃?
The working temperature of LCD screens generally does not reach 90 ° C, mainly due to the balance between LCD materials, other components (such as backlight and driver chips), and cost and reliability, which limits their high temperature resistance performance. The following figure clearly illustrates these core limiting factors and their inherent connections:
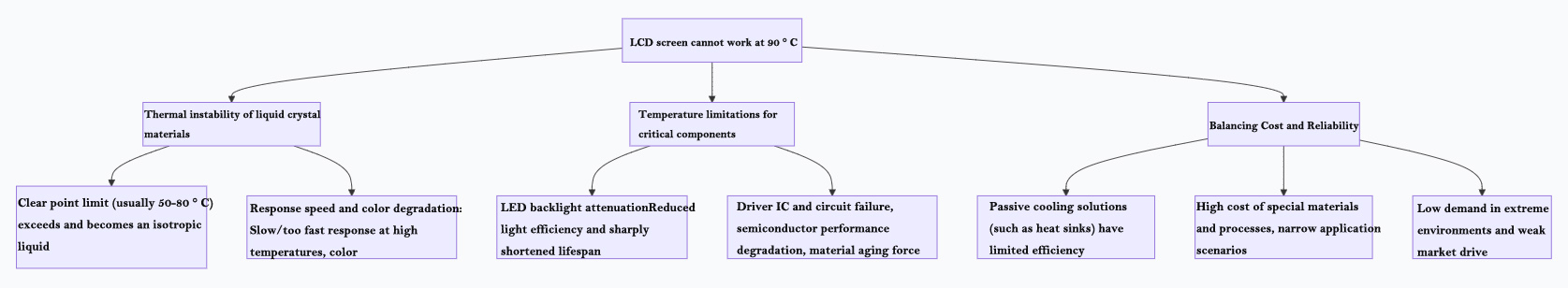
Detailed explanation of core limiting factors
The specific manifestations of several core factors shown in the above figure are as follows:
The thermal instability of liquid crystal materials themselves is the fundamental limitation.
Clear point limitation: Liquid crystal is a substance between liquid and crystal, and its core characteristics (such as ordered arrangement) only exist within a specific temperature range. When the temperature rises to the clear point (usually 50 ° C to 80 ° C), liquid crystal molecules will become ordinary isotropic liquids, lose their optical modulation ability, and the screen will turn black or display abnormally. This process is reversible after cooling. For example, the clear point of early TN screens may be around 70 ° C.
Performance degradation: Even below the clear point, high temperature can cause changes in liquid crystal viscosity, resulting in slower or faster response speed and potentially causing color shift.
2. Temperature limitations for other key components:
LED backlight system: This is one of the main heat sources. Conventional LEDs experience a decrease in luminous efficiency and a sharp reduction in lifespan under sustained high temperatures. The light guide plate and optical film (such as brightening film) in the backlight module may also deform and turn yellow at high temperatures.
Driver ICs and circuits: Semiconductor components such as TFTs and driver chips may experience performance degradation and increased leakage current at high temperatures, which may lead to display errors. Polarizers and optical adhesive materials such as OCA glue are prone to delamination, bubble formation, or aging and yellowing at high temperatures.
3. Balance between cost, reliability, and market demand:
To achieve a high-temperature working range close to 90 ° C, special liquid crystal materials, high-temperature LEDs, military grade chips, and heat-resistant adhesive materials need to be used, supplemented by efficient active heat dissipation (such as fans and heat pipes), which will lead to exponential cost growth.
The upper temperature limit of the working environment for the vast majority of consumer electronics and industrial application scenarios, such as car dashboards and outdoor industrial screens, is typically between -30 ° C and 80 ° C. For a very small number of applications that do require high temperatures above 90 ° C (such as near certain engine compartments or special industrial environments), the market is niche and typically uses non liquid crystal technology (such as monochrome vacuum fluorescent display screens VFD, OLED, or specially designed special screens).
Practical solutions for dealing with high temperature environments
If your project does face high temperature challenges, you can consider the following directions:
Choose industrial grade "wide temperature screen": Clearly state the wide temperature requirements to professional LCD module manufacturers. They can provide products with a wider working temperature range (such as -40 ° C to 85 ° C) by optimizing materials and production processes, which is currently the mainstream high-end industrial solution that balances technology and cost.
Understanding the technological limit: Currently, the maximum operating temperature of conventional LCD technology in the industry is usually around 90 ° C to 100 ° C, and it is often accompanied by compromises such as high cost, short lifespan, or low performance.
Consider alternative technologies: For extreme environments exceeding 100 ° C, it is necessary to evaluate non liquid crystal solutions such as OLED (which has slightly better high-temperature resistance but still has lifespan issues), monochrome VFD, or reflective technology-based electronic paper.
If you want to know information about wide temperature products of specific sizes, or have specific application scenarios (such as the highest temperature in the device installation environment), I can provide more specific selection ideas.
Wide temperature LCD screen:https://www.auo-lcd.com/products/auo-lcd-screen/
AUO LCD Display:https://www.auo-lcd.com/products/auo-lcd-screen/




